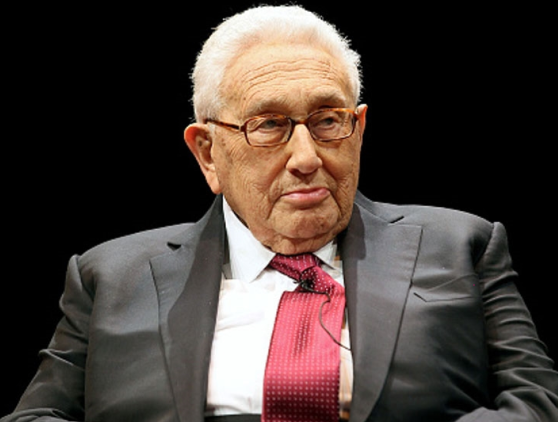
Henry Kissinger is a well-known American politician, diplomat, and geopolitical strategist who served as Secretary of State and National Security Advisor under Presidents Richard Nixon and Gerald Ford.
Henry Kissinger’s Biography, Wiki and Quick Facts
| Celebrated Name | Henry Kissinger |
|---|---|
| Age | 99 Years Old |
| Nick Name | Henry |
| Birth Name | Henry Alfred Kissinger |
| Birth Date | 1923-05-27 |
| Gender | Male |
| Profession | Politician |
| Birth Nation | Germany |
| Nationality | German |
| Place Of Birth | Fürth, Bavaria |
| Mother | Paula Kissinger |
| Father | Louis Kissinger |
| Brothers | Walter |
| Ethnicity | Mixed |
| Religion | Judaism |
| College / University | Harvard College |
| Marital Status | MArried |
| Wife | Nancy Maginnes, Ann Fleischer (Ex-Wife) |
| Children | Elizabeth, and David |
| Sexual Orientation | Straight |
| Residence | Kent |
| Height | 1.75 meters |
| Weight | 71 Kg |
| Eye Color | Green |
| Hair Color | White |
| Body Type | Large |
| Net Worth | $10 million |
| Source of Wealth | Political Career |
| Links | Wikipedia |
Despite receiving the Nobel Peace Prize for his role in negotiating a cease-fire in Vietnam, Kissinger remains a divisive figure in American politics due to his association with controversial policies such as the United States’ involvement in the 1973. Chilean military coup and the United States’ support for Pakistan during the Bangladesh Liberation War.
He is also credited with pioneering détente strategy with the Soviet Union, arranging ties with China, engaging in shuttle diplomacy to end the Yom Kippur War in theMiddle East, and negotiating the Paris Peace Accords to end the United States’ involvement in the Vietnam War. Nancy Maginnes, his second wife, is his wife.
Kissinger, born as a Jewish refugee in Germany in 1923, fled Nazi persecution and moved in the United States in 1938. Following his undergraduate and graduate degrees from Harvard University, he founded Kissinger Associates, an international geopolitical consulting firm.
Despite being named the most efficient U.S. Kissinger remains a divisive figure, revered by some and vilified by others for his acts and policies during his term in government, according to a survey of prominent international relations researchers.
How much is Henry Kissinger’s net worth? Wealth and Earnings of Henry
Henry Kissinger is a well-known political figure who has held a number of key posts in the United States administration. As of April 2023, he had a net worth of more than $10 million, mostly from his political career. He has also worked as a geopolitical consultant and author, adding to his fortune. Despite his enormous wealth, Kissinger is known for leading a simple life and has expressed happiness with his money.
Kissinger has been acknowledged for his expertise in international affairs and diplomacy throughout his career. He has written multiple books on these subjects, which have added to his net worth. He has also worked as a consultant for many governments and corporations, receiving large payments for his services. Despite his affluence, Kissinger is known for his humility and is widely respected for his commitment to public service.
You may also read the latest bio and wiki of American Politician: Donald Trump
Who are Henry Kissinger’s parents? Early Life, Childhood, College, Family and Education of Henry
Henry Kissinger was born on May 27, 1923, in Fürth, Bavaria, Germany, as Heinz Alfred Kissinger. His parents were housewife Paula (née Stern; 1901-1998, Leutershausen) and schoolteacher Louis Kissinger (1887-1982), and he had a younger brother, businessman Walter (1924-2021).
Kissinger’s family was of German Jewish heritage, and his great-great-grandfather Meyer Löb acquired the surname Kissinger in 1817 after the Bavarian spa town of Bad Kissingen. He celebrated his 99th birthday in 2022 and is of German nationality with a mixed ethnic heritage. The rise of Nazi Germany and its persecution of Jews affected his early existence.
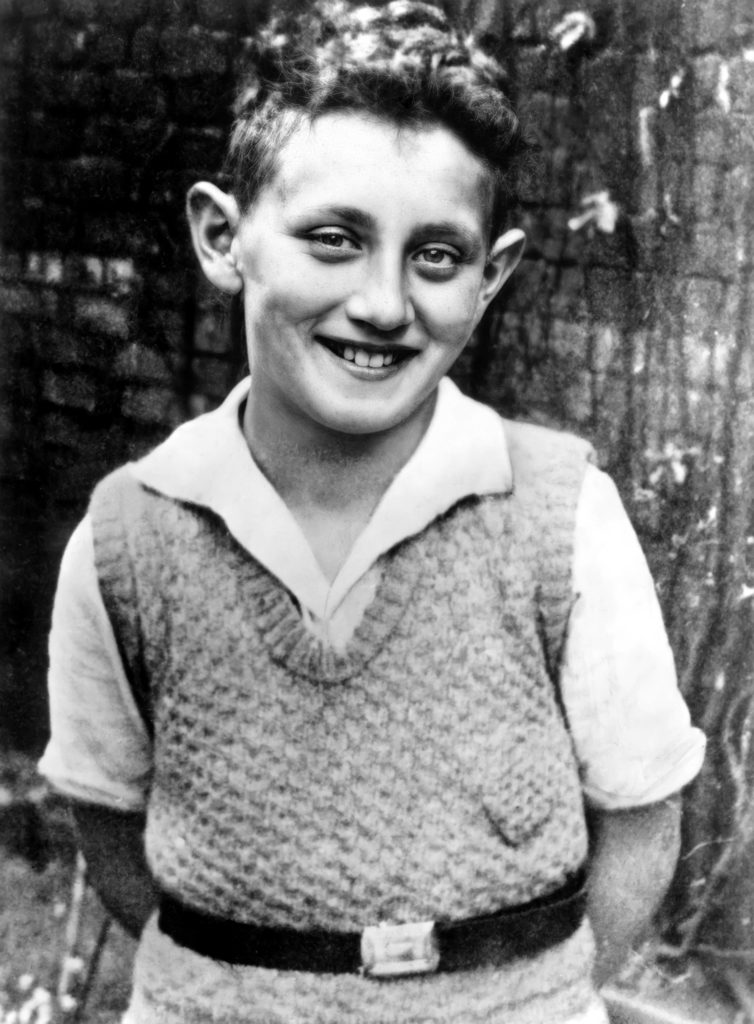

He played soccer for one of Germany’s premier clubs as a child, but his family fled Germany in 1938 due to the Nazis’ anti-Semitic legislation. Kissinger quickly integrated into American society in New York City, but retained his German accent due to his timidity.
As a part-time student at City College of New York, he excelled academically, but his studies were cut short in 1943 when he was drafted into the United States Army. Army. Despite Kissinger’s efforts to downplay the impact of his Nazi persecution on his politics, many academics feel it affected his realist approach to foreign affairs.
Also Read: Leonid Yakovlevich Gozman Net Worth, Bio, Early Life, Education, Career, Endorsements, Awards, Relationship Status, Scandal, Body Measurements, Social Media
During WWII, Henry attended basic training at Camp Croft in Spartanburg, South Carolina, and at the age of 20, he became a naturalized US citizen while stationed there. After the army halted Kissinger’s engineering program at Lafayette College, he was deployed to the 84th Infantry Division, where he met fellow immigrant Fritz Kraemer.
Kraemer recognized Kissinger’s German proficiency and intelligence and arranged for him to be posted to the division’s military intelligence branch. During the Battle of the Bulge, Kissinger served with the division and volunteered for dangerous intelligence operations. Because of his fluency in German, Kissinger was put in charge of the administration of the city of Krefeld during the American advance into Germany.
Kissinger was subsequently transferred to the Counter Intelligence Corps (CIC), where he rose to the rank of sergeant as a CIC Special Agent. He was given command of a team in Hanover tasked with tracking down Gestapo agents and other saboteurs, for which he received the Bronze Star.
Kissinger was appointed commandant of the Bensheim metro CIC unit, Bergstrasse district of Hesse, in June 1945, with responsibility for the district’s denazification. Kissinger remained a civilian employment after leaving the army, teaching at the European Command Intelligence School at Camp King.
Latest Bio: Annie Linskey – Who is the husband of Political Journalist Annie? Age, Bio, Wiki, Career, Net Worth, Family & News
In 1950, Henry Kissinger graduated from Harvard College with the top honors of summa cum laude and Phi Beta Kappa in political science. He was mentored by William Yandell Elliott and lived in Adams House. His senior thesis, The Meaning of History: Reflections on Spengler, Toynbee, and Kant, which delved into history and philosophy, was nearly 400 pages lengthy and set the current thesis length limit of 35,000 words.
Kissinger went on to acquire his MA and Ph.D. degrees in 1951 and 1954, respectively, from Harvard University. In 1952, while still a graduate student, he worked as a consultant to the director of the Psychological Strategy Board and launched Confluence, a magazine. During this time, Kissinger expressed an interest in becoming an FBI spy. Peace, Legitimacy, and Equilibrium (A Study of Castlereagh and Metternich’s Statesmanship) was the title of his PhD dissertation.
How did Henry Kissinger’s career go? Politican Career of Henry Alfred Kissinger
- Following his academic accomplishments, Kissinger remained at Harvard as a member of the Department of Government faculty and directed the Harvard International Seminar from 1951 to 1971. He also worked as a consultant for the National Security Council’s Operations Coordinating Board and the Arms Control and Disarmament Agency.
- In 1957, he published Nuclear bombs and Foreign Policy, in which he advocated for the frequent deployment of tactical nuclear bombs to win conflicts. In the same year, he published A World Restored, which studied balance-of-power politics in post-Napoleonic Europe. Kissinger went on to become the director of the Harvard Defense Studies Program and co-founder of the Center for International Affairs, as well as a foreign policy advisor to Nelson Rockefeller’s presidential aspirations.
- He met Richard Nixon for the first time in 1967 and was originally dismissive of him, but then changed his opinion and phoned a Nixon campaign staffer to express his willingness to assist Nixon in winning the presidency. Kissinger was appointed National Security Advisor when Nixon was elected President in 1969.
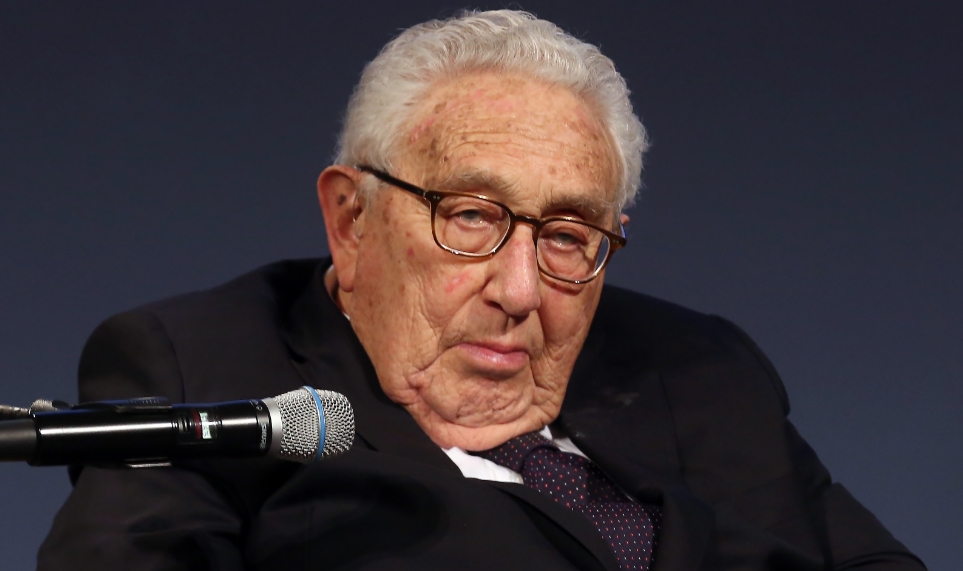

- Kissinger held high-level posts in the United States government, including National Security Advisor and Secretary of State under Presidents Richard Nixon and Gerald Ford. Following the death of George Shultz in 2021, he is presently the sole remaining member of Nixon’s Cabinet. Kissinger and Nixon had a strong relationship that has been compared to the partnerships of Woodrow Wilson and Colonel House or Franklin D. Roosevelt and Harry Hopkins, in which the State Department played a secondary role in foreign policy creation.
ALso Read the biography of : Donald Newhouse
- Kissinger was initially uninterested in repairing relations with China, but Nixon was the driving force behind the reconciliation. Kissinger traveled to China twice in secret in 1971 to meet with Premier Zhou Enlai, and the main topic of discussion was Taiwan. Kissinger agreed to Zhou’s demand that the United States acknowledge Taiwan as a genuine part of China, promising to withdraw US soldiers from Taiwan when Sino-American relations improved.
- During his time as President Richard Nixon’s National Security Adviser, Henry played a key role in the Vietnam War peace talks. Kissinger’s participation with Indochina began when he worked as a foreign policy consultant for the White House and State Department. In 1967, he brokered a peace initiative between Washington and Hanoi. Kissinger favored a negotiation strategy in which the United States and North Vietnam signed an armistice and agreed to withdraw their forces from South Vietnam.
- Kissinger was disappointed by the stalled Paris peace talks in late 1969, which were stymied by the South Vietnamese delegation’s obstructionism. As a result, he initiated secret peace discussions in Paris with North Vietnamese officials, which the South Vietnamese were unaware of. Kissinger and North Vietnamese negotiator Le Duc Tho signed a peace deal on January 27, 1973, calling for the complete departure of all US forces from Vietnam by March in exchange for North Vietnam releasing all US prisoners of war.
You may also read the biograph of : Ivanka Trump
- Kissinger consented to an interview with journalist Oriana Fallaci in 1972, which turned out to be a flop. Kissinger called Vietnam a “useless war,” compared himself to a cowboy, and hinted that he preferred supper with Lê c Th over Nguyn Văn Thiu. Nixon was furious and refused to meet Kissinger for several weeks. Kissinger later described it as his “most disastrous conversation” with the press. Kissinger was portrayed by Fallaci as a “intellectual adventurer” and self-styled Metternich. Despite claims of “selective genocide” against Bengali academics and independence activists during the Bangladesh Liberation War in 1971, Nixon and Kissinger backed Pakistani dictator Yahya Khan.
- Nixon removed Secretary of State Rogers in 1973 and replaced him with Kissinger, who later admitted to overlooking the importance of the Egyptian-Saudi partnership. To keep Nixon from interfering, Kissinger delayed alerting him about the start of the Yom Kippur War. He committed to replenish Israel’s losses in equipment after the conflict, but wanted to postpone arm shipments in order to boost the chances of reaching an agreement.
- Kissinger was concerned about the Soviet Union’s dominance in the Persian Gulf. Iraq and Iran had a fight over the Shatt-al-Arab River in 1969, and Iraq severed diplomatic relations with Iran in 1971. Nixon and Kissinger visited Tehran in 1972 and agreed to back Kurdish insurgents fighting for independence from Iraq. Kissinger considered Iraq’s Baathist dictatorship as a potential threat to the US and saw Iran as America’s surrogate in the Persian Gulf. Supporting Iran and the Peshmerga was regarded as the most effective counterweight.
Also Read: Maria Ohisalo – Who is the husband of Finnish Politician Maria? Age, Bio, Wiki, Career, Net Worth and Facts
- Kissinger received criticism in 1974 for the United States’ handling of the Greek junta’s coup and the Turkish invasion of Cyprus. The State Department was informed of the coup ahead of time, leading to claims of US complicity. Kissinger was a target of anti-American sentiment in Greece and Cyprus, and he expressed dissatisfaction with his handling of the issue years later.
- Kissinger was implicated in the failed attempt to prevent Chile’s socialist Salvador Allende from being inaugurated, as well as the subsequent military coup led by Pinochet. He also revoked an official US letter to Chile warning of political assassination. Kissinger has been accused of participating in Operation Condor, a clandestine operation of political repression and killing.
- Despite its racist and corporatist dictatorship, Kissinger’s State Department was more supportive to Portugal than prior administrations. In 1971, they successfully renewed the lease on the American military base in the Azores, and they thanked Portugal for using it to equip Israel during the Yom Kippur War. Kissinger was concerned after the regime’s demise about the rapid decolonization plan and the inclusion of the Portuguese Communist Party in the new government. Indonesia invaded East Timor, which had declared independence, in 1975.
Read Also: Does Kulsoom Nawaz Was Pakistani Politician and Pakistan’s First lady? Net Worth, Bio & Death Cause
- Kissinger and President Ford did not protest to the proposed annexation and only wanted it done swiftly during a meeting with Indonesian President Suharto. From 1975 to 1981, the invasion killed over a fifth of the Timorese population. Despite the invasion, the United States continued to sell weaponry to Indonesia. During the 1970 Cienfuegos Crisis, Kissinger halted the Soviet submarine facility in Cuba and mulled air attacks against Cuba in 1976.
- He advocated for the return of Spanish Sahara to Morocco and deceived President Ford into believing that the International Court of Justice favored Morocco. He was also active in strengthening relations with Mobutu Sese Seko, Zaire’s ruler, which he described as a policy achievement.
Later Career work of American Politician Henry Kissinger
- After Nixon resigned in the Watergate affair, Kissinger’s influence in Gerald R. Ford’s new presidential administration waned, and he was replaced as National Security Advisor by Brent Scowcroft during the November 1975 “Halloween Massacre” cabinet reshuffle. When Democrat Jimmy Carter defeated Republican Gerald Ford in the 1976 presidential election, Kissinger resigned as Secretary of State. Kissinger, on the other hand, continued to participate in policy bodies such as the Trilateral Commission, as well as political consulting, speaking, and writing engagements.
- Kissinger criticized Jimmy Carter’s foreign policy, saying in 1980 that it “managed the extraordinary feat of having, at the same time, the worst relations with our allies, the worst relations with our adversaries. And the most serious upheavals in the developing world since the end of World War II.” After leaving office in 1977, Kissinger was offered an endowed chair at Columbia University. However, there was student protest to the appointment, which became a topic of media debate, and as a result, Columbia canceled the appointment.
- Kissinger remained engaged in academia and politics despite the cancellation of his post. Kissinger Associates was created in 1982, and he is a partner in affiliate Kissinger McLarty Associates alongside Mack McLarty, former chief of staff to President Bill Clinton. He also served on the board of directors of Hollinger International. A Chicago-based media conglomerate, and was a director of Gulfstream Aerospace as of March 1999.
RElated News: Rosa Silver Net Worth, Bio, Early Life, Education, Career, Endorsements, Awards, Relationship Status, Scandal, Social Media
- In November 2002, President George W. Bush chose him to chair the newly constituted National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Upon the United States to examine the September 11 attacks. When asked about potential conflicts of interest, Kissinger stood down as chairman on December 13, 2002, rather than divulge his business client list. Kissinger was paid $5 million in the Rio Tinto espionage case of 2009-2010 to counsel the multinational mining firm on how to separate itself from an employee who had been arrested in China for bribery.
- Despite some criticism, Kissinger has remained active in international politics, advocating for a world free of nuclear weapons and furthering this agenda through the Nuclear Threat Initiative. Kissinger received the American Patriot Award from the National Defense University Foundation in December 2008 “in recognition of his distinguished career in public service.”
- Former US Secretary of State and National Security Advisor Henry Kissinger is well-known for his divisive views on international policy. During the Yugoslav Wars, Kissinger chastised the United States for recognizing Bosnia and Herzegovina as an independent state and advised against Western intervention. He also condemned the Rambouillet Agreement, viewing it as an inducement to begin bombing. During the Iraq War, Kissinger persuaded President George W. Bush and Vice President Dick Cheney that defeating the insurgency was the only viable exit route. Kissinger backed the 2003 invasion of Iraq but condemned the administration for entering with too few soldiers, mishandling ties with specific allies. And disbanding the Iraqi Army as part of the de-Baathification process.
Kissinger has also expressed his opinions on India and China.
See Also: Christina Pushaw – Who is Christina Pushaw? Age, Bio, Wiki, Ethnicity, Net Worth, Husband and Political Career?
- He regarded India as a US ally with similar goals and interests. In his book On China, he traced the trajectory of Sino-American relations. And outlined the obstacles to a cooperation based on “genuine strategic trust” between the two countries. He remarked in a 2018 interview with the Financial Times. That he believes China wants to reclaim its historic role as the Middle Kingdom and become “the principal adviser to all humanity.” His stance on China has sparked debate, with some questioning his desire to deal with a country accused of human rights violations and strong territorial ambitions.
- Former US Secretary of State Henry Kissinger proposed a diplomatic solution to Russia’s 2022 invasion of Ukraine in May 2022. Which would restore the status quo ante bellum, including relinquishing Crimea and sections of Donbas to Russia. Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy. On the other hand, rejected this idea, stating that Ukraine would only commit to peace if Russia returned Crimea and the Donbas region. Kissinger reaffirmed his position in July 2022, indicating that he backed a ceasefire line on the 24 February border. And that Ukraine should not give up any land that it possessed when the war began.
- Kissinger pushed in January 2023 for more US backing until the borders of 24 February were recognized, at which point negotiations would commence. He also voiced his appreciation for President Zelensky and speculated that NATO membership for Ukraine could be a logical result of the peace effort.
Henry Kissinger Honors and Awards
Kissinger and Le Duc Tho were awarded the Nobel Peace Prize jointly in 1973 for their work on the Paris Peace Accords. Which resulted in the withdrawal of American soldiers from the Vietnam War. (Le Duc Tho declined to accept the award, claiming that such “bourgeois sentimentalities” were not for him and that peace had not been achieved in Vietnam.) Kissinger donated his prize money to charity, did not attend the award ceremony, and later offered to return his prize medal after South Vietnam was overrun by North Vietnamese forces 18 months later.
- Kissinger was awarded the U.S. The Senator John Heinz Award for Outstanding Public Service by an Elected or Appointed Official is presented yearly by Jefferson Awards.
- Kissinger was the first honorary member of the Harlem Globetrotters in 1976.
- Kissinger was awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom by President Gerald Ford on January 13, 1977.
- Kissinger received the National Book Award in History in 1980 for the first volume of his memoirs, The White House Years.
- Kissinger was one of twelve recipients of the Medal of Liberty in 1986.
- He was appointed an honorary Knight Commander of the Most Distinguished Order of St Michael and St George in 1995.
- Kissinger was awarded the Sylvanus Thayer Award at the United States Military Academy at West Point in 2000.
- Kissinger was made an honorary member of the International Olympic Committee in 2002.
- Kissinger received Israel’s President’s Medal on March 1, 2012.
- Lighthouse International presented Kissinger with the Henry A. Grunwald Award for Public Service in October 2013.
- Kissinger was a member of the Rothermere American Institute’s Founding Council at the University of Oxford.
Read More:
- From 2014 until 2017, Kissinger was on the board of Theranos, a health technology company.
- In 2009, he earned the Union League Club of New York’s Theodore Roosevelt American Experience Award.
- In 2018, he was named Honorary Chair of the Bloomberg New Economy Forum’s advisory board.
- He was also honored with the Ellis Island Medal of Honor.
Kissinger is a member of the following organizations:
- Aspen Institute
- Atlantic Council
- Bilderberg Group
- Bohemian Club
- Council on Foreign Relations
- Center for Strategic and International Studies
- World.Minds
Who is the wife of American Politician Henry Kissinger?
On February 6, 1949, Henry Kissinger married Ann Fleischer, with whom he had two children, Elizabeth and David. They divorced in 1964, however. On March 30, 1974, he married Nancy Maginnes, with whom he has been married ever since. The couple currently splits their time between Kent, Connecticut and New York City.

David Kissinger, Kissinger’s son, has had a successful career in television production. And first as an executive with NBC Universal Television Studio until becoming president of Conaco, Conan O’Brien’s production business, in 2005. Despite his high-profile work, Kissinger and his wife appear to live a peaceful life free of major disruptions.
What is Henry Kissinger’s height?
While Henry Kissinger’s physical appearance is not as important as his achievements in politics. And diplomacy, he does have a dominating presence. He has a huge body type and stands 1.75 meters tall, which is around 5 feet 9 inches. Despite his advanced age, Kissinger maintains a healthy weight of 71 kg. He has distinguishing traits, such as pale green eyes and white hair. And that have been synonymous with his public image over time.
Kissinger’s physical appearance was not a key influence in his success. But his dominating presence and reputation surely aided him in achieving many of his diplomatic goals during his career. Henry had coronary bypass surgery in February 1982, at the age of 58. He currently has a healthy body.
You Should Know These Henry Kissinger Facts.
- In a 1973 interview, Kissinger stated that diplomacy was his favorite game.
- In 1955, he became a consultant to the National Security Council’s Operations Coordination Board, as well as the Council on Foreign
- Relations’ study director in nuclear weapons and foreign policy.
- His family was Jewish and German.
- He was awarded Israel’s President Medal in 2012.
- In 1973, he was appointed Secretary of State by Nixon.
- He was part in the United States’ détente policy with the Soviet Union.
- He is well-known for his use of Realpolitik.






